A. Overall Description of Pain Points in Enterprise Production Management
Enterprise production management often encounters a series of complex and intertwined challenges. These problems not only affect the daily operation of the enterprise but also have a long - term impact on its development and competitiveness in the market.
- Low production efficiency: Manual processes, outdated equipment, and inefficient workflow designs can lead to long production cycles and low output. For example, in some traditional manufacturing enterprises, workers still rely on paper - based work orders and manual data entry, which is time - consuming and error - prone.
- High production costs: Excessive raw material waste, high labor costs, and inefficient energy use contribute to increased production costs. Additionally, poor inventory management can lead to overstocking or shortages, both of which can increase costs.
- Quality control difficulties: Ensuring consistent product quality is a major challenge. Inadequate inspection processes, lack of real - time monitoring, and poor traceability can result in defective products reaching the market, damaging the company's reputation.
- Poor communication and collaboration: Siloed departments, lack of information sharing, and ineffective communication channels can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and inefficiencies in the production process. For instance, the production department may not be aware of changes in customer orders, leading to production of non - compliant products.
In summary, these pain points in enterprise production management are interrelated and can have a cumulative negative impact on the enterprise's performance. Solving these problems requires a comprehensive and systematic approach.
B. Case Analysis of Pain Points in Enterprise Production Management
1. Low production efficiency
Low production efficiency is a common pain point in many enterprises. In traditional manufacturing, the reliance on manual processes for tasks such as production scheduling, material handling, and quality inspection can slow down the entire production line. For example, in a furniture manufacturing company, the production of each piece of furniture involves multiple steps, from cutting the wood to assembling and finishing. If these steps are not well - coordinated, workers may have to wait for materials or equipment, leading to idle time.
Take the case of a small - scale furniture factory. Before implementing a digital solution, they used paper - based work orders to assign tasks to workers. This process was not only time - consuming but also prone to errors. For instance, a worker might misinterpret a hand - written instruction, leading to rework. After adopting a digital production management system, the factory was able to streamline its production process. Workers could receive tasks directly on their mobile devices, and real - time data on production progress was available to managers. As a result, the production cycle was reduced by 30%, and overall efficiency increased significantly.
2. High production costs
High production costs can erode a company's profit margins. In the manufacturing industry, raw material costs often account for a large proportion of the total production cost. Inefficient inventory management can lead to overstocking, which ties up capital and increases storage costs. On the other hand, shortages of raw materials can lead to production delays and additional costs for expedited shipping.
For example, a chemical manufacturing company used to order raw materials in large quantities to take advantage of volume discounts. However, this often led to overstocking, and some materials would expire before they could be used. After implementing a just - in - time inventory management system, the company was able to reduce its inventory levels by 40% while still ensuring a continuous supply of raw materials. This not only reduced storage costs but also minimized waste.
3. Quality control difficulties
Maintaining consistent product quality is essential for customer satisfaction and brand reputation. In industries such as electronics and automotive manufacturing, even a small defect can have serious consequences. Traditional quality control methods, such as random sampling and manual inspection, may not be sufficient to detect all defects.
Consider a smartphone manufacturing company. With the increasing complexity of smartphone components, it is becoming more difficult to ensure quality through traditional inspection methods. Before using a digital quality control system, the company faced a high rate of defective products. After implementing a real - time monitoring system that uses sensors and cameras to inspect each component during the production process, the defect rate was reduced by 50%. The system can detect even the smallest defects and immediately alert the production line workers to take corrective actions.
4. Poor communication and collaboration
In large enterprises, poor communication and collaboration between departments can lead to significant inefficiencies. For example, in a manufacturing company with multiple departments such as production, sales, and R & D, lack of communication can result in the production of products that do not meet customer requirements.
A clothing manufacturing company faced this problem. The design department would create new clothing styles without fully consulting the production department. As a result, the production department might face difficulties in sourcing the right materials or using the appropriate production techniques. After implementing a collaborative platform, all departments could share information in real - time. The design department could get feedback from the production department during the design process, and the sales department could provide information on customer preferences. This improved communication led to a 20% increase in customer satisfaction.
C. Product Introduction
1. Traditional ERP Systems
Traditional ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are comprehensive software solutions that integrate various business processes, including production management, finance, human resources, and supply chain management. These systems can help enterprises streamline their operations by providing a centralized database and standardized processes.
For example, an ERP system can automate the production planning process by considering factors such as inventory levels, customer orders, and production capacity. It can also generate real - time reports on production progress, allowing managers to make informed decisions. However, traditional ERP systems often require significant upfront investment in terms of software licenses, implementation, and training. They can also be complex to customize, which may not be suitable for enterprises with rapidly changing business needs.
2. MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems)
MES systems focus specifically on the production floor. They provide real - time monitoring and control of production processes, from raw material intake to finished product output. MES systems can track production data, such as machine status, worker performance, and quality control results.
For instance, in a semiconductor manufacturing plant, an MES system can monitor the temperature, pressure, and other parameters of each production step in real - time. If any parameter goes out of the specified range, the system can immediately alert the operators to take corrective actions. However, MES systems are often limited to the production floor and may not integrate well with other business functions outside of production.
3. No - code Platform: Wingent
Wingent is a no - code platform that offers a flexible and efficient solution for enterprise production management. It allows users to quickly build customized management systems without the need for coding skills.
D. How Wingent Solves the Pain Points in Enterprise Production Management
1. Streamlining Production Processes
Wingent enables enterprises to design and implement customized production workflows. For example, a manufacturing enterprise can use Wingent to create a digital work order system. Workers can receive work orders on their mobile devices, and they can update the progress of their tasks in real - time. This eliminates the need for paper - based work orders and manual data entry, reducing the risk of errors and improving production efficiency.
2. Cost Control
With Wingent, enterprises can implement better inventory management. The system can track raw material usage, monitor inventory levels, and generate automatic reorder alerts when stock levels are low. This helps to reduce overstocking and shortages, thereby controlling production costs. Additionally, Wingent can analyze production data to identify areas where cost - saving measures can be implemented, such as optimizing energy consumption or reducing waste.
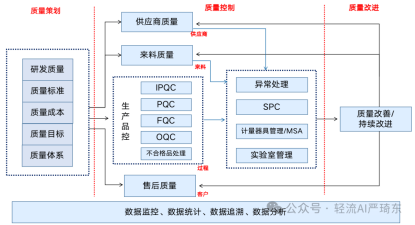
3. Quality Assurance
Wingent supports real - time quality control. It can be integrated with sensors and inspection devices to collect quality data during the production process. For example, in a food manufacturing enterprise, Wingent can be used to monitor the temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors in the production area. If any quality issue is detected, the system can immediately trigger an alert and initiate corrective actions. This ensures that only high - quality products are produced and delivered to customers.

4. Enhancing Communication and Collaboration
Wingent provides a centralized platform for information sharing and communication. All departments can access the same data and collaborate more effectively. For example, the sales department can share customer order information with the production department in real - time, and the production department can provide updates on order progress to the sales department. This improves communication, reduces misunderstandings, and enhances overall productivity.
In summary, Wingent offers a comprehensive solution to the pain points in enterprise production management. It can improve production efficiency, control costs, ensure product quality, and enhance communication and collaboration within the enterprise.
Enterprise production management pain points such as low efficiency, high costs, quality control issues, and poor communication are critical challenges that need to be addressed. Innovative solutions like Wingent provide a practical and effective way to overcome these challenges. By leveraging the capabilities of Wingent, enterprises can optimize their production processes, improve their bottom line, and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Reference: [1] 5000字详解生产质量管理:供应链、工序、检验、溯源、工具、激励、文化 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/TSQHoUsDtlWldBNkiUFbIw [2] 2小时,我搭建了一个生产管理系统,包含排程、质量、物料、设备、报工等多模块 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/G6BG0ez8vV93nBS4BhbWtQ [3] 7大维度,中小制造业企业如何选择生产管理系统? https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pm14LCcwxlHfMKRHAgkEFQ [4] 生产计划、排产调度、现场管控、质量管理怎么做?一文看懂生产全流程管理 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/DR2qqMLPuA4ADOOJvtuLPw [5] 7大维度,中小制造业企业如何选择生产管理系统? https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pm14LCcwxlHfMKRHAgkEFQ
